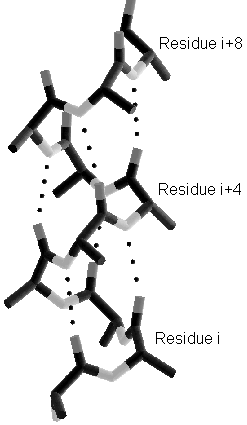
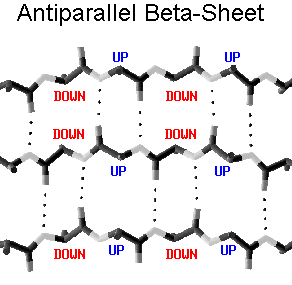
Highly cooperative systems of hydrogen bonds govern the framework of the 3D protein structure. We will have a quick look at the most prominent ones: the alpha helix and the beta sheet (made from different beta strands). Note how side chains i, i+3, i+4 end up on the same side along the helix (helix rises 3.6 residues per turn). Note also how side chains go up and down along the beta strands, and thus do not see each other, but see side chains of the neighboring strands.
The positioning of the side chains on helices or sheets have profound implications: they can convey global properties to the secondary/tertiary structure elements which allows these elements to pack together in the protein. Hydrohpobic elements will pack against each other in the core of the protein while hydrophilic elements will be exposed. Proteins have:
Right-handed alpha Helix


![]() 1.3 From 3D Motifs to Multimeric Proteins
1.3 From 3D Motifs to Multimeric Proteins